Agentic Infrastructure Attack Surface
Comprehensive analysis of security vulnerabilities in multi-agent AI systems. Understand the attack surface, threat vectors, and security controls needed to protect agentic infrastructure.
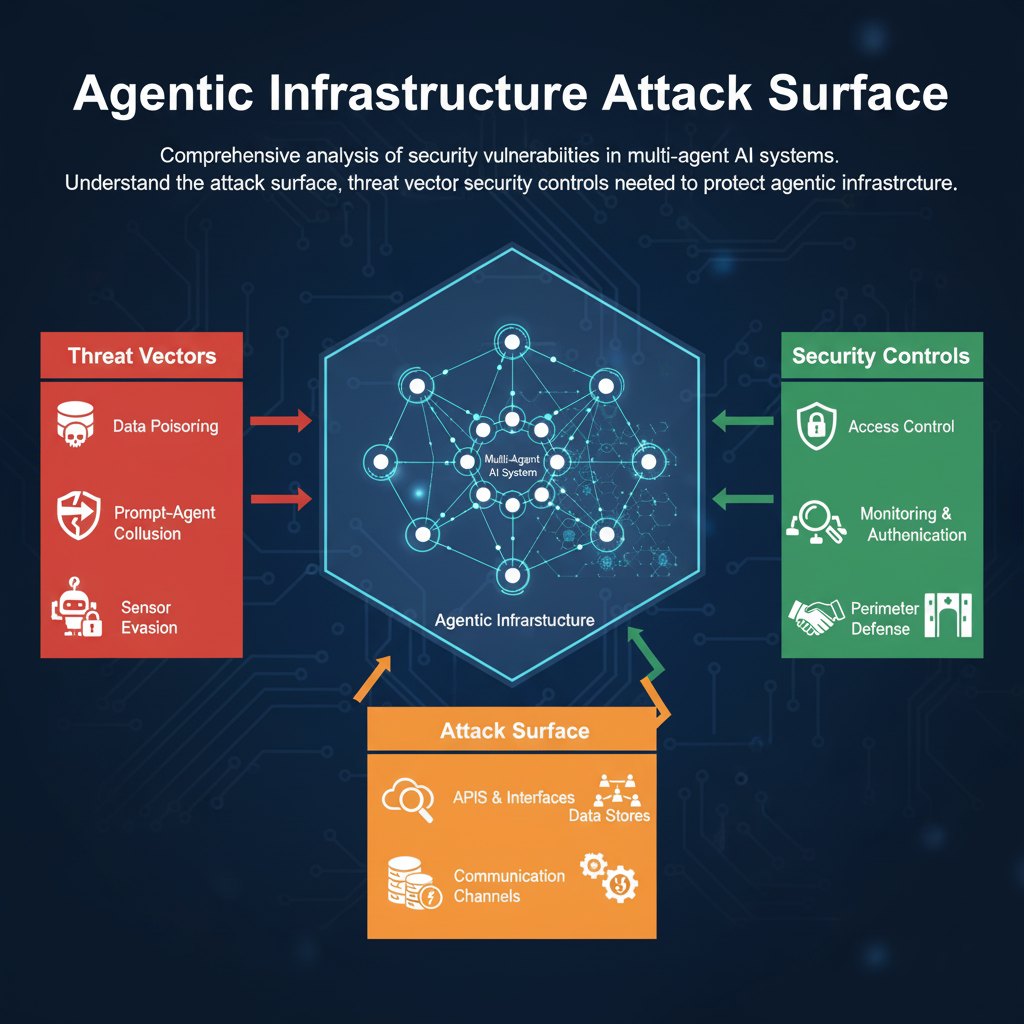
Understanding Agentic Infrastructure
Agentic AI systems represent a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence, where multiple autonomous agents collaborate to solve complex problems. However, this distributed architecture introduces a significantly expanded attack surface compared to traditional monolithic AI systems.
Data poisoning, prompt-agent collusion, and sensor evasion attacks targeting agent systems
APIs, interfaces, data stores, and communication channels vulnerable to exploitation
Access control, monitoring, authentication, and perimeter defense mechanisms
Critical Attack Surface Areas
Eight key areas where agentic infrastructure is vulnerable to attacks
Key Threats
- Message interception and tampering
- Agent impersonation attacks
- Protocol exploitation
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
Security Controls
- End-to-end encryption for agent messages
- Mutual authentication between agents
- Message signing and verification
- Secure communication protocols (TLS 1.3+)
Key Threats
- Context poisoning attacks
- Memory corruption
- State manipulation
- Data leakage between agents
Security Controls
- Memory isolation and sandboxing
- Access control policies
- State validation and integrity checks
- Encrypted memory storage
Key Threats
- Orchestration hijacking
- Workflow manipulation
- Task injection attacks
- Resource exhaustion
Security Controls
- Orchestrator authentication
- Workflow validation
- Rate limiting and quotas
- Audit logging of orchestration events
Key Threats
- Privilege escalation
- API abuse and over-permissioning
- Tool injection attacks
- Unauthorized system access
Security Controls
- Principle of least privilege
- Tool access whitelisting
- API rate limiting
- Runtime permission validation
Key Threats
- Code injection attacks
- Sandbox escape
- Arbitrary code execution
- Container breakout
Security Controls
- Secure sandboxing (gVisor, Firecracker)
- Code signing and verification
- Runtime security monitoring
- Container security hardening
Key Threats
- Infrastructure misconfiguration
- Network segmentation bypass
- Resource hijacking
- Supply chain attacks
Security Controls
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) security
- Network segmentation
- Security group policies
- Regular security audits
Key Threats
- Prompt injection via UI
- Social engineering attacks
- Credential theft
- Session hijacking
Security Controls
- Input validation and sanitization
- Multi-factor authentication
- Session management
- User activity monitoring
Key Threats
- Log tampering
- Monitoring blind spots
- Alert fatigue exploitation
- Telemetry data exposure
Security Controls
- Immutable logging
- Centralized log management
- Real-time anomaly detection
- Secure telemetry collection
Real-World Attack Scenarios
Understanding how attackers exploit agentic infrastructure vulnerabilities
Attack Chain:
- 1Initial compromise of a low-privilege agent
- 2Lateral movement through agent communication channels
- 3Privilege escalation via orchestration layer
- 4Full system compromise and data exfiltration
Impact
Complete system takeover, data breach, service disruption
Mitigation
Zero-trust architecture, agent isolation, continuous monitoring
Attack Chain:
- 1Inject malicious content into shared memory
- 2Poisoned context consumed by multiple agents
- 3Agents make decisions based on corrupted data
- 4Cascading failures across agent network
Impact
Incorrect decisions, data corruption, system instability
Mitigation
Context validation, memory isolation, integrity checks
Attack Chain:
- 1Identify over-permissioned agent
- 2Craft prompts to abuse tool access
- 3Execute unauthorized operations
- 4Exfiltrate sensitive data or modify systems
Impact
Data breach, unauthorized system modifications, compliance violations
Mitigation
Least privilege, tool access auditing, runtime monitoring
Security Framework
A comprehensive approach to securing agentic infrastructure across the lifecycle
- Threat modeling for agent architecture
- Security requirements definition
- Trust boundary identification
- Attack surface analysis
- Secure coding practices
- Security testing integration
- Dependency scanning
- Code review with security focus
- Infrastructure hardening
- Network segmentation
- Access control implementation
- Security monitoring setup
- Continuous security monitoring
- Incident response procedures
- Regular security assessments
- Patch management
Resources & Next Steps
Tools and guidance to secure your agentic infrastructure
Explore tools for monitoring and securing agent infrastructure
View ToolsStep-by-step roadmap for enterprise agent security
Read GuideLearn to secure agentic systems with hands-on courses
Browse Courses